The Petri dish, a staple in laboratories around the world, serves multiple purposes that extend beyond its simple design. This document explores the various applications, historical significance, and science behind the Petri dish, shedding light on why it is an essential tool in microbiology, cell culture, and various scientific research fields.
A Petri dish is one of the most iconic tools in microbiology and scientific research. It is a shallow, cylindrical, transparent dish made of glass or plastic, used primarily to culture microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and cells.
Table of Contents
What is the Purpose of a Petri Dish?
A petri dish, also known as a petri plate, is a shallow, cylindrical, flat dish made of glass or clear plastic that is used primarily in laboratories for microbiological studies. Its design and material make it an essential tool in various scientific fields, including biology, medicine, and environmental science. This article explores the purpose of a petri dish, its applications, and its significance in scientific research.
Structure and Design of a Petri Dish
A typical Petri dish consists of two parts: a shallow, flat bottom and a lid that fits snugly over the top. The bottom of the dish with a growth medium, such as agar, which provides the necessary nutrients for microorganisms to thrive. The transparent nature of the dish allows scientists to observe the growth and behavior of cultures without disturbing them.

Materials Used
Petri dishes can be made from various materials, including:
- Glass: Reusable and autoclavable, glass Petri dishes are ideal for high-temperature applications and can be sterilized easily.
- Plastic: Disposable plastic Petri dishes are convenient for single-use applications and are often pre-sterilized to prevent contamination.
Sizes and Variations
Petri dishes come in various sizes, typically ranging from 35 mm to 150 mm in diameter. Some variations include:
- Multi-well plates: These are similar to Petri dishes but contain multiple wells for the simultaneous culturing of different samples.
- Specialized dishes: Some manufacturers design Petri dishes for specific applications, incorporating unique coatings or compartments to accommodate different types of cultures.
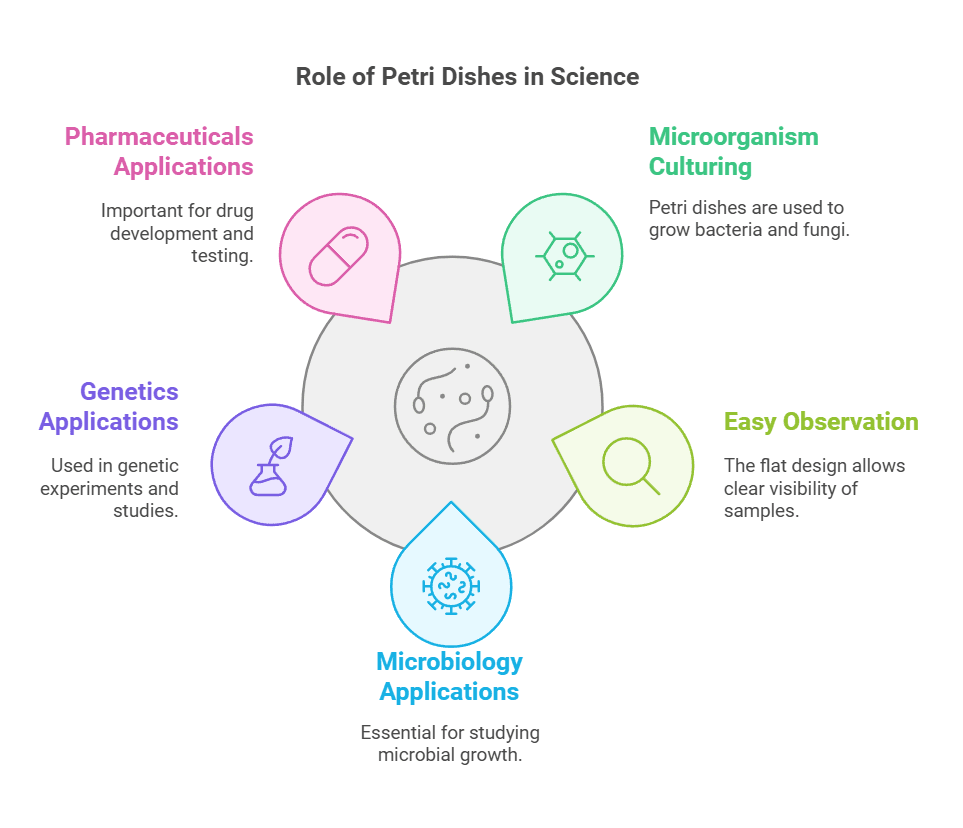
Primary Uses of Petri Dishes
Microbial Culture
One of the primary purposes of a Petri dish is to culture microorganisms. By providing a controlled environment, researchers can grow bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms for study. This process is essential for:
- Identifying pathogens: By isolating and culturing bacteria from clinical samples, scientists can identify infectious agents and determine appropriate treatments.
- Studying microbial behavior: Researchers can observe how microorganisms interact with their environment, including their growth patterns, metabolic activities, and responses to various stimuli.
Cell Culture
Use petri dishes to grow cells for tissue engineering applications, aiming to create artificial tissues for transplantation or regenerative medicine.. This involves growing eukaryotic cells, such as animal or plant cells, in a controlled environment. Key applications include:
- Drug testing: Scientists can use cell cultures to evaluate the effects of new drugs on specific cell types, providing valuable insights into their efficacy and safety.
- Tissue engineering:
Environmental Studies
Researchers also employ petri dishes in environmental studies to assess microbial diversity and activity in various ecosystems. By collecting soil or water samples and culturing microorganisms in Petri dishes, researchers can:
- Monitor pollution: By analyzing microbial communities in contaminated environments, scientists can assess the impact of pollutants and develop bioremediation strategies.
- Study biodiversity: Petri dishes allow researchers to isolate and identify different microbial species, contributing to our understanding of ecosystem health and resilience.
Food Safety Testing
In the food industry, Petri dishes play a crucial role in ensuring food safety. Microbiologists use them to culture and identify pathogens in food samples, helping to prevent foodborne illnesses. Common applications include:
- Testing for pathogens: By culturing food samples on selective media, researchers can detect harmful bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
- Quality control: Researchers use petri dishes in routine testing to monitor the microbial quality of food products, ensuring they meet safety standards.
Best Practices for Using Petri Dishes
To ensure successful outcomes when using petri dishes, you should follow certain best practices:
- Sterilization: Always sterilize petri dishes before use to prevent contamination from unwanted microorganisms.
- Aseptic Technique: Employ aseptic techniques when handling samples to maintain sterile conditions throughout the experiment.
- Proper Incubation: Ensure that you follow the appropriate incubation times and temperatures for the specific organism you are culturing.
- Labeling: Clearly label each dish with relevant information (date, sample type) to avoid confusion during analysis.
Conclusion
Petri dishes are indispensable tools in scientific research and laboratory work due to their versatility and effectiveness in culturing microorganisms and cells. Their applications span various fields, such as microbiology, medicine, environmental science, and education. Understanding their purpose not only highlights their importance but also underscores the foundational role they play in advancing scientific knowledge and improving public health outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, so will the methods associated with using Petri dishes, ensuring they remain relevant tools for future discoveries.
FAQs
What is a Petri Dish?
A Petri dish, also known as a Petri plate or culture plate, is a shallow, transparent, lidded dish typically made of glass or plastic. Researchers primarily use petri dishes in laboratories to cultivate microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, and to conduct various biological experiments.
Where Are Petri Dishes Used?
Petri dishes find applications across various fields due to their versatility:
- Microbiology Laboratories: They are fundamental tools for studying bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- Clinical Laboratories: Used for diagnosing infections by culturing pathogens from patient samples.
- Research Institutions: Employed in studies related to genetics, biotechnology, and environmental science.
- Educational Institutions: Commonly used in schools and universities for teaching purposes and practical experiments.
- Food Industry: Used for quality control to detect microbial contamination in food products.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Essential for drug development processes, including testing antibiotic efficacy.
What types of experiments can be conducted using a Petri dish?
Petri dishes are used in various types of experiments, such as:
- Growing bacterial or fungal cultures
- Testing antibiotic resistance
- Observing microbial interactions and behavior
- Studying plant tissue culture and cell growth
- Testing chemical reactions and biological responses
Uses of Petri Dishes in Laboratories
Petri dishes have a wide range of applications in laboratory settings. Here are some of the primary uses:
Are Petri dishes safe to use?
Petri dishes are generally safe to use when handled according to laboratory safety protocols. However, the contents within them (such as bacteria or fungi) may pose health risks. Always practice proper sterilization techniques, use gloves, and follow safety guidelines to prevent contamination or accidental exposure.
How are Petri dishes sterilized?
To prevent contamination, researchers must sterilize Petri dishes, particularly reusable glass ones. They can achieve this through autoclaving, which involves steam sterilization under pressure, or by using a dry-heat sterilizer. In contrast, disposable cell culture flask come pre-sterilized and are ready for immediate use.
You May Also Read
- What is a Petri Dish?
- Why use Petri dishes?
- What is the Difference Between a Petri Dish, a Petri Flask, and a Petri Plate?
- What are the differences between TC culture dishes and Non-TC culture dishes?
- The Untold Secrets of Tissue Culture Vessels
If you enjoyed this article, please subscribe to our YouTube channel. We provide product video tutorials. You can also follow us on Instagram and Facebook to stay up to date with new updates, news and special deals.