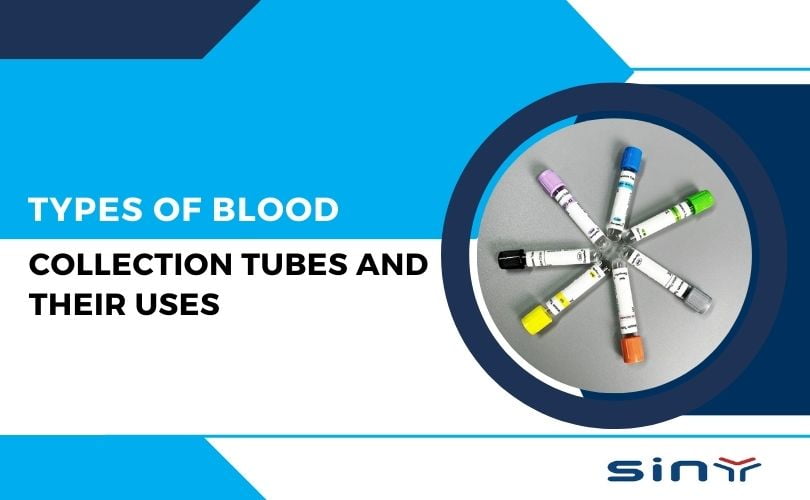
Blood collection tubes are specialized containers designed to collect and store blood samples for laboratory testing. These tubes are made from plastic or glass and come in various sizes and colors, each representing a different additive. The choice of the tube depends on the type of test to be performed, as different additives interact with blood in specific ways to either prevent clotting, promote clotting, or preserve certain elements within the blood.

Table of Contents
- 1 Types of Blood Collection Tubes and Their Uses
- 2 Conclusion
- 3 FAQs
- 3.1 What are blood collection tubes?
- 3.2 What do the different colors of blood collection tubes indicate?
- 3.3 What are the common types of blood collection tubes?
- 3.4 Why is it important to use the correct blood collection tube?
- 3.5 Can the blood collection tubes expire?
- 3.6 What tests are commonly performed using each type of blood collection tube?
Types of Blood Collection Tubes and Their Uses
Blood collection tubes are critical tools in medical laboratories for obtaining and storing blood samples for various tests. Each tube type has specific additives and characteristics that determine its use. Below are the different types of blood collection tubes and their respective uses:
Red-Top Tube
- Additive: None (plain tube)
- Uses:
- Serum collection for various tests.
- Commonly used for chemistry panels, serology, and blood bank tests.
- Ideal for tests that do not require anticoagulation, as the blood will clot, allowing serum to be separated for analysis.
Green-Top Tube
- Additive: Heparin (anticoagulant)
- Uses:
- Plasma collection for tests requiring anticoagulated blood.
- Frequently used for blood gas analysis and certain chemistry tests.
- Suitable for tests that require immediate processing, as heparin prevents clotting.
Purple-Top Tube
- Additive: EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)
- Uses:
- Primarily used for hematology tests, such as complete blood counts (CBC).
- Essential for blood bank tests, including crossmatching and typing.
- EDTA tube preserves cellular components, making it ideal for tests that analyze blood cells.
Gray-Top Tube
- Additive: Sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate
- Uses:
- Primarily used for glucose testing, as sodium fluoride inhibits glycolysis.
- Suitable for lactate and alcohol testing.
- It preserves glucose levels for accurate measurement.
Yellow-Top Tube
- Additive: ACD (acid-citrate-dextrose) solution
- Uses:
- Used for blood cultures and genetic testing.
- ACD is effective for preserving blood components for longer periods.
- Ideal for tests requiring whole blood or plasma.
Pink-Top Tube
- Additive: EDTA (similar to lavender tube)
- Uses:
- Specifically designed for blood bank testing.
- Used for crossmatching and antibody screening.
- Ensures accurate results in transfusion medicine.
Blue-Top Tube
- Additive: Sodium citrate
- Uses:
- Used for coagulation studies, such as PT (prothrombin time) and aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time).
- Sodium citrate tube acts as an anticoagulant, preserving the blood’s clotting properties for accurate testing.
- It is important for assessing bleeding disorders and monitoring anticoagulant therapy.
Each type of blood collection tube is color-coded for easy identification, and the choice of the tube depends on the specific laboratory tests required. Proper handling and mixing of the tubes post-collection are essential to ensuring accurate test results.
Conclusion
Blood collection tubes are indispensable in modern medicine, facilitating the accurate collection and analysis of blood samples. Understanding the different types of tubes and their specific uses is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure optimal patient care. Proper training and adherence to protocols regarding blood collection can significantly enhance the reliability of laboratory results, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
For more detailed information on blood collection tubes and their applications, visit Sinymedical.
FAQs
What are blood collection tubes?
Blood collection tubes are specialized containers used to collect, store, and transport blood samples for laboratory testing. They come in various types, each designed for specific tests based on the additives they contain.
What do the different colors of blood collection tubes indicate?
The color of the tube cap indicates the type of additive present in the tube, which determines its use. For example, red tubes typically contain no additives for serum collection, while lavender tubes contain EDTA for hematology tests.
What are the common types of blood collection tubes?
- Red-Top Tube: No additive tube, is used for serum tests.
- Light Blue-Top Tube: Contains sodium citrate, used for coagulation tests.
- Green-Top Tube: Contains heparin; used for plasma tests.
- Lavender or Purple-Top Tube: Contains EDTA, used for hematology tests.
- Gray-Top Tube: Contains sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate, used for glucose testing.
Why is it important to use the correct blood collection tube?
Using the correct tube is crucial for obtaining accurate laboratory results. Each tube’s additives can affect the sample’s composition, and using the wrong tube can lead to erroneous results or sample contamination.
Can the blood collection tubes expire?
Yes, blood collection tubes have expiration dates printed on their labels. Using expired tubes can compromise the integrity of the sample and lead to inaccurate test results.
What tests are commonly performed using each type of blood collection tube?
- Red-Top Tube: chemistry tests, serology, and immunology.
- Light Blue-Top Tube: Coagulation tests (e.g., PT, aPTT).
- Green-Top Tube: blood gas analysis and routine chemistry tests.
- Lavender or Purple-Top Tube: Complete blood counts (CBC) and blood bank tests.
- Gray-Top Tube: Glucose testing and lactic acid measurement.