Blood sample analysis plays a crucial role in modern medical diagnostics, with many tests relying on the correct type of collection tube to ensure accurate results. Among the most widely used tubes in hematology and other tests are EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) tubes. These tubes contain an anticoagulant that helps preserve the shape and integrity of the blood cells, making them ideal for specific types of laboratory examinations.
In this article, we will explore the top five lab tests requiring EDTA tubes and their significance in clinical diagnostics.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is a EDTA Tubes?
- 2 Lab Tests That Require EDTA Tubes
- 3 Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- 4 Blood Smear Analysis
- 5 Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
- 6 G6PD Screening and Assay
- 7 Coagulation Studies (PT/APTT)
- 8 Characteristics of EDTA Tubes
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 FAQs
- 10.1 What are EDTA tubes used for?
- 10.2 Why is EDTA preferred over other anticoagulants?
- 10.3 What color are EDTA tubes?
- 10.4 How should EDTA tubes be handled after blood collection?
- 10.5 Can EDTA tubes be used for coagulation studies?
- 10.6 What is the shelf life of EDTA tubes?
- 10.7 How much blood is needed for tests using EDTA tubes?
- 11 You May Also Read
What is a EDTA Tubes?
EDTA Tube is a chelating agent that binds to calcium ions in the blood. Calcium is essential for coagulation; by binding to it, EDTA prevents blood from clotting. This property makes EDTA particularly useful in hematological tests where accurate measurement of blood cells is crucial.
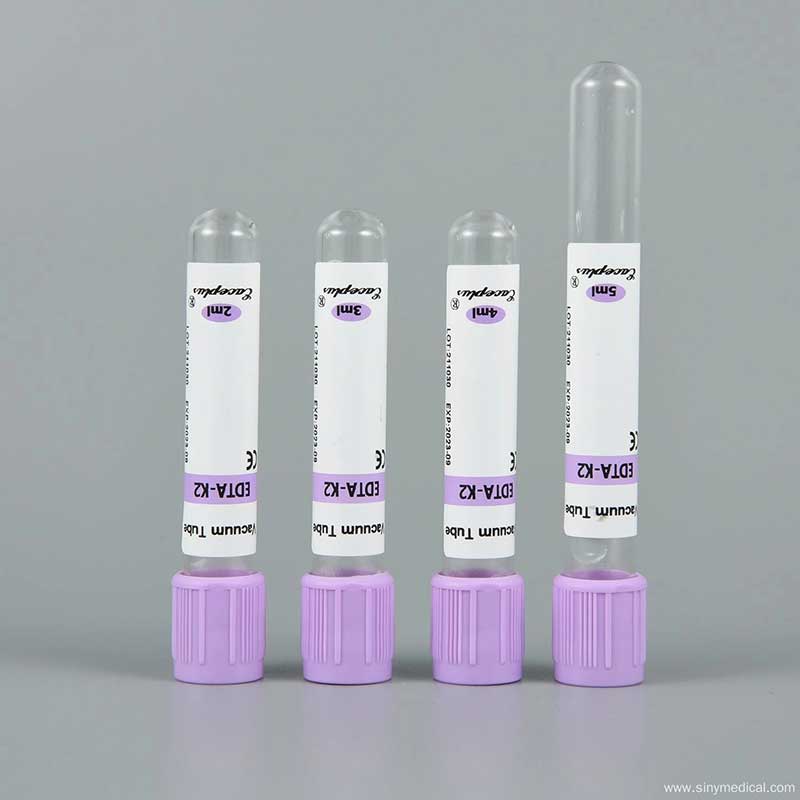
Lab Tests That Require EDTA Tubes
EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) tubes, commonly recognized by their purple or lavender tops, are essential in various laboratory tests due to their anticoagulant properties. EDTA works by chelating calcium ions in the blood, which prevents coagulation and allows for the accurate analysis of blood components.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Healthcare providers frequently order the Complete Blood Count (CBC) as one of the most common blood tests in clinical practice. It provides critical information about the cellular components of blood, including:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Measures the number and health of red blood cells.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Assesses immune function by counting different types of white blood cells.
- Hemoglobin: Evaluates oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Hematocrit: Determines the proportion of blood volume occupied by red blood cells.
- Platelets: Measures clotting potential.
Why EDTA?
EDTA is the preferred anticoagulant for CBC because it preserves cell morphology and prevents clotting, allowing for accurate cell counts and differentiation. The test typically requires 2.0 – 2.5 mL of whole blood collected in an EDTA tube.
Blood Smear Analysis
- A technician performs a microscopic examination of a thin layer of blood spread on a glass slide during blood smear analysis. This test is crucial for diagnosing various hematological disorders, including Anemia.
- Leukemia
- Thrombocytopenia
Why EDTA?
Clinicians use EDTA tubes to collect samples for blood smears because they prevent clotting and maintain cell integrity during transport to the lab. The process involves preparing a smear from an EDTA-stabilized sample, which allows for a detailed examination of cell morphology and identifying abnormalities.Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
Hemoglobin electrophoresis identifies different types of hemoglobin in the blood, playing a vital role in diagnosing hemoglobinopathies like sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
Why EDTA?
This test requires an EDTA tube because it preserves the stability of hemoglobin variants during analysis. Collect 2.0 – 2.5 mL of blood in an EDTA tube to keep the hemoglobin in a liquid state, allowing for accurate separation and identification using electrophoresis techniques.
G6PD Screening and Assay
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency screening is essential for identifying individuals at risk for hemolytic Anemia, particularly after exposure to certain medications or infections.
Why EDTA?
EDTA tubes are utilized for G6PD testing to prevent clotting and maintain enzyme activity in the sample. The test typically requires 2.0 – 2.5 mL of whole blood collected in an EDTA tube. Proper handling is crucial; transport samples promptly to avoid degrading G6PD activity.
Coagulation Studies (PT/APTT)
While coagulation studies often use citrate tubes, specific tests such as activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) can also utilize EDTA tubes, depending on laboratory protocols.
Why EDTA?
In some cases, especially when assessing certain coagulation factors or performing specific molecular tests related to coagulation disorders, EDTA tubes may prevent clotting while preserving plasma integrity for accurate results.
Characteristics of EDTA Tubes
- Color Coding: Healthcare professionals typically identify EDTA tubes by their lavender or purple tops. This color coding allows them to quickly recognize the type of tube and its specific purpose.
- Volume: These tubes come in various sizes, usually ranging from 2 mL to 10 mL, depending on the volume of blood required for testing.
- Additives: The most common form of EDTA used in these tubes is K2 EDTA (potassium salt) or K3 EDTA (tri potassium salt). K2 EDTA is more commonly used due to its better stability and lower risk of hemolysis.
Conclusion
EDTA tubes play a vital role in various laboratory tests by preventing coagulation and preserving cellular components necessary for accurate analysis. The top five tests requiring these tubes—Complete Blood Count (CBC), Blood Smear Analysis, Hemoglobin Electrophoresis, G6PD Screening and Assay, and Coagulation Studies—highlight the importance of proper sample collection and handling in clinical diagnostics.
By understanding the significance of each test and the role of EDTA, healthcare professionals can ensure reliable results that aid in effective patient management and treatment decisions.
FAQs
What are EDTA tubes used for?
Laboratories primarily use EDTA tubes for blood collection in tests that require anticoagulation, such as complete blood count (CBC), blood smear analysis, hemoglobin electrophoresis, and G6PD screenig.
Why is EDTA preferred over other anticoagulants?
Laboratories prefer EDTA because it chelates calcium ions effectively, preventing clotting without significantly altering blood cell morphology. This preservation is crucial for accurate hematological analyses.
What color are EDTA tubes?
EDTA tubes typically have a lavender or purple top, which helps identify them as containing the EDTA anticoagulant.
How should EDTA tubes be handled after blood collection?
After collecting blood, gently invert the EDTA tubes several times to mix the blood with the anticoagulant. Then, store them upright and transport them to the laboratory promptly to preserve the sample’s integrity.
Can EDTA tubes be used for coagulation studies?
Laboratories mainly use citrate EDTA tubes for coagulation studies, but they may use EDTA tubes for specific tests based on their protocols. However, it’s essential to follow the guidelines provided by the testing laboratory.
What is the shelf life of EDTA tubes?
The shelf life of EDTA tubes varies by manufacturer but typically ranges from 6 months to 1 year when stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Always check the expiration date on the tube packaging.
How much blood is needed for tests using EDTA tubes?
The blood volume required varies by test but typically ranges from 2 mL to 10 mL. Filling the tube to the indicated line is essential to ensure accurate results.
You May Also Read
- What are EDTA K3 and EDTA K2?
- Why EDTA is Used as the Additive in Purple Top Tubes?
- A Complete Guide to EDTA Tubes
- The Purple EDTA Tube in the Blood Collection Tube
If you enjoyed this article, please subscribe to our YouTube channel. We provide product video tutorials. You can also follow us on Instagram and Facebook to stay up to date with new updates, news and special deals.