Blood bags are critical medical devices for collecting, storing, and transfusing blood and blood components. The manufacturing process involves several steps to ensure the bags meet strict quality and safety standards.
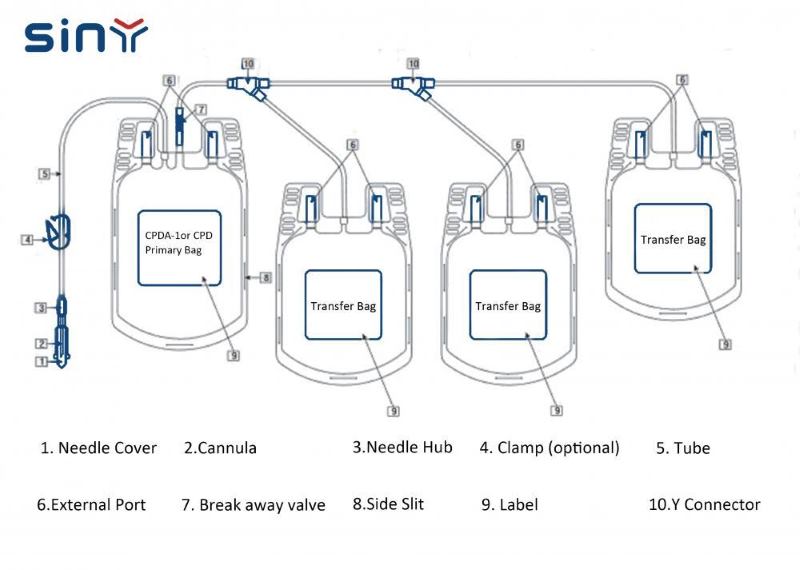
The blood bag system is a disposable biomedical device designed to collect, store, transport, and transfuse human blood and its components. This system typically includes one or more bags connected by tubes and a needle, a needle cover, a clamp, and other necessary components.
Table of Contents
What are Blood Bags?
These disposable biomedical transparent flexible polyvinyl chloride(PVC) containers are designed to collect, process, and store whole blood and blood components.
- The main components of a blood bag system include. A deformable, hermetically sealed plastic bag to collect the blood.
- A diaphragm-sealed delivery tube for infusion
- A collecting line made of flexible tubing
- A needle, needle cover, and clamps
These components are designed to be flexible enough to fill blood, transfer components, and complete emptying without venting. Visit: What is a blood bag?
Manufacturing Process
The production of blood bag systems involves several key steps:
Compounding: The process begins by compounding PVC material with various additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, and lubricants. This formulation is crucial for manufacturing the bags and tubes.
Extrusion: The extruder transforms the PVC compound into a sheet by pushing it through a die. After extrusion, workers immediately slit, cut, and send the sheet to the welding section. They also use PVC compounds to produce donor and transfer tubes.
Injection Molding: Injection molding produces components such as transfusion ports, needle covers, and clamps.
- The components are dried in a drying oven after ultrasonic cleaning.
- A needle holder also secures needles.
Anticoagulant Solution: Mix the required ingredients in pyrogen-free distilled water to prepare the anticoagulant solution. Follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) throughout the process. After preparation, fill the blood bags with the solution.
Welding: The manufacturer assembles blood bags using a high-frequency welding technique. They position-size PVC sheets between electrodes, apply high voltage to heat, and seal the PVC with remarkable speed. The transfusion ports, donor, and transfer tubes are correctly positioned and welded to form an integral part of the blood bag system, all done with impressive efficiency.
Sterilization: A steam autoclave sterilizes the blood bags, ensuring they meet sterility standards. Blood bag sterilization refers to eliminating or inactivating microorganisms from blood bags and their components, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Printing and Labeling: The blood bags contain essential information such as lot numbers, expiration dates, and other relevant details.
Final Packaging: The sterilized and labeled blood bags are placed in protective outer packaging, such as pouches or boxes, to maintain sterility during storage and transportation. The packaged bags are then ready for distribution to healthcare facilities.
There are different types of blood bags
The blood bag system consists of a blood donation bag, a blood donor tube (a needle with a needle cover), a pierceable, non-sealable blood transfusion tank, and forceps for collecting whole blood, storing it, and transfusing the blood components.
Single blood bag
Single Blood Bags collect, preserve, and transfusion Whole Human Blood.
- Designed for whole blood collection
- Contains 63 ml CPDA-1/CPD+SAGM anticoagulant solution
- Capacity ranges are 200–500 ml.
- Tamper-proof needle and standard donor tubing

Double blood bag
The double blood bag system separates two components from whole blood. This double system includes one primary bag with anticoagulant CPDA-1 Solutions USP and one empty satellite bag.
- Designed for separating whole blood into plasma and red cells
- Reduces the possibility of contamination
- The primary bag contains CPDA-1 or CPD anticoagulant solution
- Primary Bag Capacity:150ml、250ml、350ml、450ml、500ml
- Anticoagulant /Additive Solution: CPDA or CPD
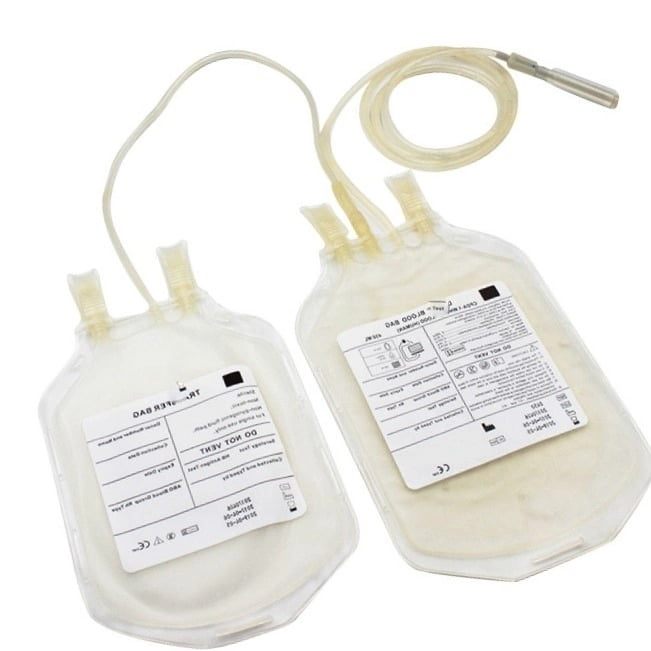
Triple Blood Bag
Triple blood bag for separating packed cells, plasma, and platelets
- Donor Needle Gauge Size: Available in 16G or 17G
- Anticoagulant /Additive Solution: CPDA or CPD
- Primary Bag Capacity: 150ml、250ml、350ml、450ml、500ml

Quadruple Blood Bag
Separate packed cells, plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate in this quadruple blood bag
Final summary
Manufacturing blood bags is a complex and highly regulated process that requires meticulous attention to detail at every stage. From material selection to quality control, each step is essential to producing a reliable and safe product. Siny Medical advances, the industry continues to innovate, improving blood bag production’s safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
FAQs
How to make a blood bag?
To make a blood bag manufacturer compound medical-grade PVC, extrude it into sheets, and then form it into bags. They assemble and weld the components together, sterilize them, and inspect them before packaging.
What material is used to make blood bags?
Manufacturers make blood bags from medical-grade Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), which offers flexibility, durability, and safety for storing blood.
How do you prepare a blood bag?
To prepare a blood transfusion, fill it with an anticoagulant solution, sterilize it, and ensure it meets quality standards before using it in medical procedures.
What is the role of anticoagulant solution in blood bags?
The anticoagulant solution prevents the blood from clotting inside the bag. The preparation involves mixing specific constituents in pyrogen-free distilled water, ensuring the blood remains liquid and safe for transfusion or further processing.