The syringe, an essential medical instrument, has significantly changed since its invention. These small, underestimated tools play an essential role in medical diagnostics, treatment, and care. Different designs, tailored to specific applications, ensure precision and safety. As part of this article, we examine the many types of syringes, their unique features, and their diverse uses, highlighting their indispensable place in modern healthcare.
Table of Contents
What is a Syringe?
A syringe injects liquid medications into the body as a medical instrument. It is a hollow tube with a plunger at one end and a nozzle at the other. The plunger forces liquid out of the syringe and into the patient.
Different Types of Syringes
Syringes come in different sizes, shapes, and styles. They are made from various materials, including plastic, glass, and metal. Additionally, syringes come in disposable and reusable varieties.
Size: 0.5ML, 1ML, 3ML, 5ML, 10ML, 20ML , 50ML, 60ML, 100ML, 150ML
Disposable Self-Destructing Syringe
Disposable Self-Destructing Syringes are designed to prevent the spread of disease, Single-use syringes offer a one-time solution by breaking apart after a single use. In contrast, reusable syringes support multiple uses and require cleaning between each use.
Mechanism
A disposable self-destructing syringe prevents reuse, which is crucial in preventing infection from spreading. A mechanism locks the plunger or disables the syringe after a single use of these syringes.
Advantages
The primary advantage of self-destructing syringes is that they reduce the risk of infection transmission. The devices are especially useful in countries with high infection rates or limited medical resources, where it may be challenging to ensure the sterility of medical instruments.
Applications
Immunization programs, especially in developing countries, commonly use these syringes. Their design ensures each injection is safe and prevents reuse, minimizing the risk of spreading blood-borne diseases..
Disposable Luer Lock Syringe
The design of disposable Luer Lock syringes prevents cross-contamination by securely locking the syringe tip in place after inserting the needle. This feature prevents accidental reuse of the disposable luer lock syringe, avoiding the spread of harmful pathogens.
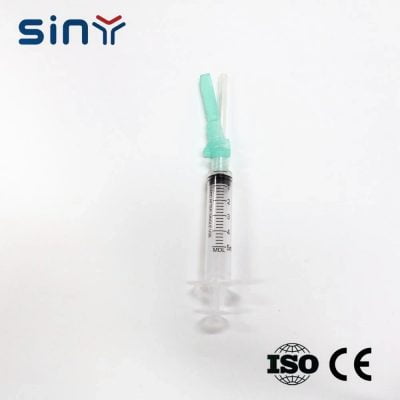

Mechanism
Luer lock syringes feature a secure twist-lock mechanism that ensures a tight connection between the needle and the syringe. Medication administration is precise and safe with this design, preventing accidental needle dislodging.
Advantages
Healthcare professionals favor luer lock syringes for their reliability and safety. A secure connection reduces the risk of needle detachment, which can lead to medication leakage or needlestick injuries. This makes them ideal for use in high-stakes medical environments.
Applications
Healthcare professionals commonly use these syringes in intravenous (IV) therapy, anesthesia, and other applications requiring precise medication delivery. Their secure connection ensures accurate and safe administration of medication.
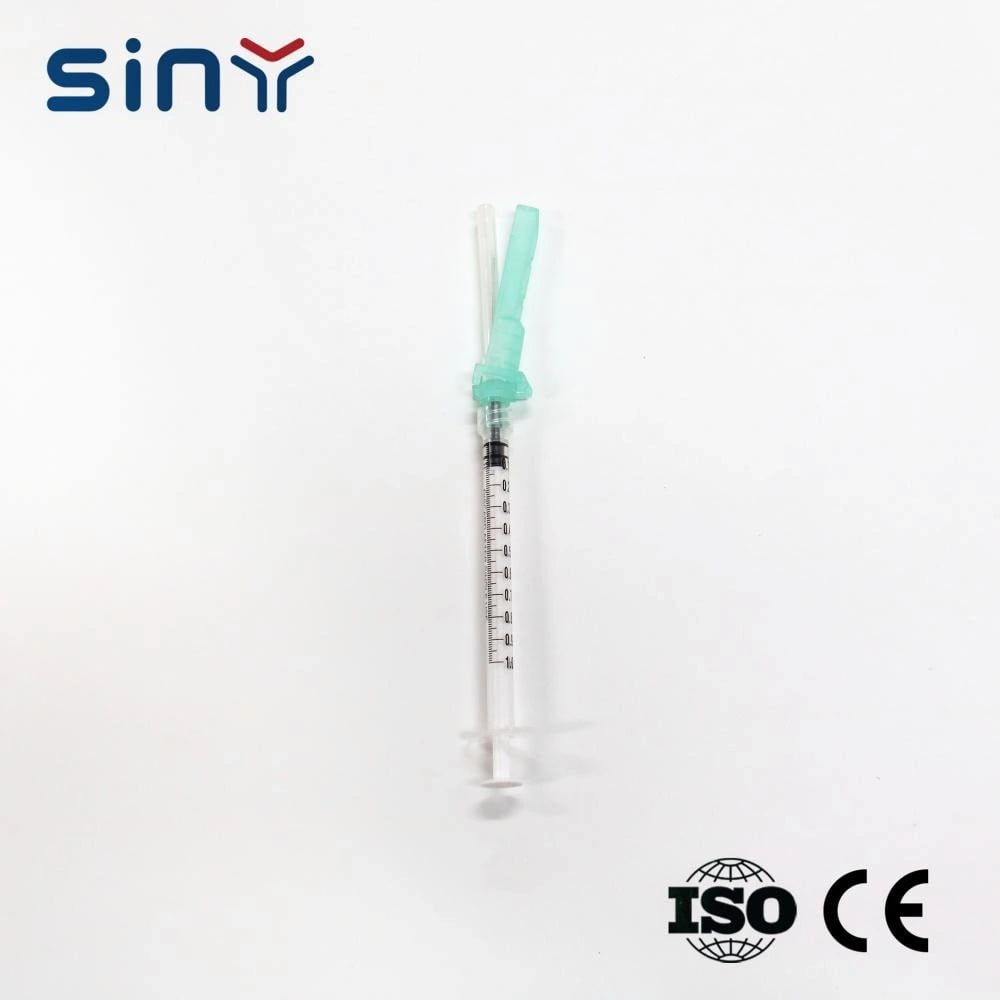
Disposable Luer Slip Syringe
Disposable Luer Slip Syringe: A user-friendly syringe with a simple push-fit needle attachment mechanism, ideal for quick and easy medication administration in non-critical applications, ensuring efficient and effective healthcare delivery.
Mechanism
The lure slip syringe, also known as the slip tip syringe, has a simple push-fit mechanism. The needle attaches and detaches quickly without twisting the syringe.
Advantages
A Luer slip syringe is a user-friendly and cost-effective device. The luer lock provides high security and allows for quick, easy needle attachment, making it suitable for various medical procedures.
Applications
Healthcare providers commonly use syringes to administer medications without a secure lock, such as subcutaneous injections or blood samples. Additionally, they are helpful when speed and ease of use are essential.
Disposable Safe Syringe
Disposable safe syringes are vital to reducing infection risk when administering medications. They prevent needle sticks and minimize cross-contamination risk by design.
Mechanism
Designers equip a safe syringe with additional safety features, such as retractable needles or needle shields, to prevent needlestick injuries and reduce infection risks.
Advantages
These syringes significantly enhance safety for both patients and healthcare workers. Safety features minimize the risk of accidental needlestick injuries, which can transmit infectious diseases.
Applications
Hospitals and clinics widely use safe syringes, especially in high-risk environments. Home healthcare settings also use them to keep caregivers and patients safe.
Disposable Vaccine Syringe
Healthcare providers use disposable vaccine syringes to administer vaccines because they are sterile, safe, and easy to carry and store. They are also cost-effective and suitable for multiple administrations.

Mechanism
Manufacturers design vaccine syringes for precision and accuracy in vaccine administration. They typically have fine needles and specific volumes to deliver the correct dosage.
Advantages
These syringes optimize vaccine administration, delivering each dose accurately and with minimal discomfort to the patient. Their design also minimizes vaccine wastage.
Applications
Immunization programs, both routine and emergency, primarily use vaccine syringes. These essential tools fight against infectious diseases, ensuring safe and effective vaccine administration
Disposable Insulin Syringe
Disposable insulin syringes are sterile and disposable, which helps reduce the risk of infection for the person administering the vaccine. Insulin syringes explicitly administer insulin to diabetes patients.
Mechanism
Manufacturers explicitly design insulin syringes to administer insulin to diabetes patients.. They have fine needles and precise calibration to ensure accurate dosing.
Advantages
These syringes allow painless and accurate insulin administration, which is crucial for diabetes management. Fine needles and clear markings help patients self-administer insulin.
Applications
Diabetes patients use insulin syringes for daily insulin injections. Medical professionals also use them to administer insulin during emergencies or hospital stays
Materials Used in Syringe Manufacture
Manufacturers use various materials to make syringes, ensuring durability, sterility, and patient comfort. Common materials include plastics, rubber, and silicone.
Plastics
Manufacturers typically use medical-grade plastics, such as durable and chemical-resistant polypropylene, to make most disposable syringes. Plastics are also lightweight and cost-effective, making them ideal for single-use syringes.
Rubber
Syringe manufacturers use rubber in plungers to create a tight seal and ensure smooth operation. Medical-grade rubber provides the flexibility and durability needed for proper syringe functionality. Medical-grade rubber is flexible and durable, ensuring that the syringe functions appropriately.
Silicone
Silicone coats syringe needles, reducing friction and making injections more comfortable for patients.
Syringe Needle Types
Syringe needles come in various gauges and lengths to suit different medical applications. The gauge of a needle refers to its diameter, with smaller numbers indicating larger diameters.
Various Gauges
Needles are available in a range of gauges, from fine needles (25–30 gauge) used for insulin injections to larger needles (18–22 gauge) used for drawing blood or administering thicker medications.
Uses
The choice of needle gauge and length depends on the type of injection and the patient’s needs. Healthcare providers use fine needles for subcutaneous and intradermal injections and larger needles for intramuscular and intravenous injections.
Syringe Sizes
Syringes come in various sizes to accommodate different volumes of medication or fluids. Standard sizes include 0.5 ML, 1 ML, 3 ML, 5 ML, 10 ML, 20 ML, 50 ML, 60 ML, 100 ML, and 150 ML syringes.
Conclusion
Syringes are essential in modern medicine, enabling the safe and effective administration of medications, vaccines, and other therapeutic agents. Understanding the different types of syringes and their specific applications is crucial for healthcare providers, ensuring patients receive the best possible care. As technology advances, syringes’ design and functionality will evolve, offering even greater safety, efficiency, and ease of use.
FAQs
What is the difference between a luer lock and a luer slip syringe?
A luer lock syringe features a twist-lock mechanism that securely attaches the needle to the syringe, preventing accidental dislodgement. A luer slip syringe, on the other hand, has a simple push-fit mechanism for attaching the needle.
How do self-destructing syringes work?
Self-destructing syringes have a built-in mechanism that locks the plunger or disables the syringe after a single use, preventing reuse and reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
Why are insulin syringes different from other types of syringes?
Designers specifically create insulin syringes for administering insulin, featuring fine needles and precise calibration marks to ensure accurate dosing and minimal discomfort for patients.
What materials are commonly used to manufacture syringes?
Manufacturers typically use medical-grade plastics, such as polypropylene, to make syringes, incorporating rubber for the plunger and silicone for needle lubrication.
How should used syringes be disposed of safely?
Used syringes should be placed in designated sharps containers and disposed of according to local regulations. This helps prevent needlestick injuries and environmental contamination.



























































