Blood collection tubes are specialized containers used to collect and store blood samples for laboratory testing. These tubes are typically made of glass or plastic and feature color-coded caps to indicate the type of additive (if any) inside. The additives preserve the blood sample, prevent clotting, or facilitate specific tests. Choosing the correct tube is crucial because the wrong tube can lead to inaccurate results, sample contamination, or delays in diagnosis.
At Siny Medical, we specialize in high-quality blood collection tubes, ensuring accuracy and reliability in laboratory testing. In this detailed guide, we will explore the key differences between red and yellow cap blood tubes, their uses, additives, and why choosing the right tube is essential for accurate test results.
Table of Contents
Red Cap Blood Tubes
Red cap blood tubes, also known as plain tubes or serum tubes, are a staple in clinical laboratories. These tubes are designed to collect blood samples for tests that require serum, the liquid portion of blood obtained after clotting. Here’s a detailed look at their characteristics and uses:

Characteristics of Red Cap Blood Tubes
- No Additives: Red cap tubes, such as the Siny Medical Red Top No Additive Vacuum Tube, typically contain no anticoagulants or preservatives. This allows the blood to clot naturally after collection.
- Material: Made from high-quality PET (plastic) or glass, ensuring durability and safety during handling.
- Vacuum System: The tubes are vacuum-sealed to draw the precise amount of blood needed, reducing the risk of over- or under-filling.
- Uses: Ideal for serum-based tests, including biochemical, immunological, and serological assays.
How Red Cap Tubes Work
When blood is collected in a red cap tube, it is allowed to clot for approximately 30–60 minutes at room temperature. After clotting, the tube is centrifuged to separate the serum (the clear, yellowish liquid) from the clot and blood cells. The serum is then used for testing. The absence of additives ensures that the sample remains uncontaminated by chemicals, making red cap tubes suitable for a wide range of diagnostic tests.
Common Tests Using Red Cap Tubes
Red cap tubes are versatile and used for various tests, including:
- Biochemical Tests: Liver function tests (e.g., ALT, AST), kidney function tests (e.g., creatinine, urea), and lipid profiles (e.g., cholesterol, triglycerides).
- Serological Tests: Tests for infectious diseases, such as hepatitis B, syphilis, and HIV.
- Immunological Tests: Hormone assays (e.g., thyroid function tests) and tumor marker detection.
- Blood Bank Testing: Certain serological tests related to blood typing and compatibility.
Advantages of Red Cap Tubes
- Simplicity: No additives mean fewer variables that could affect test results.
- Versatility: Suitable for a broad range of serum-based tests.
- Cost-Effective: Red cap tubes are often more affordable due to their lack of additives.
Best Practices for Using Red Cap Tubes
- Allow sufficient clotting time (30–60 minutes) before centrifugation to ensure proper serum separation.
- Avoid shaking the tube after collection, as this can cause hemolysis (rupture of red blood cells), which may interfere with test results.
- Centrifuge the tube at the recommended speed and duration to prevent contamination of the serum with cellular components.
For high-quality red cap tubes, explore the Siny Medical Red Top No Additive Vacuum Tube designed for reliable serum collection.
Yellow Cap Blood Tubes
Yellow cap blood tubes are specialized tubes used for tests requiring plasma, whole blood, or serum with specific additives. These tubes are known for their versatility and are a critical component in blood banking, molecular diagnostics, and other specialized testing. At Siny Medical, our Yellow Cap Blood Collection Tubes are designed to ensure sample integrity and accurate results.
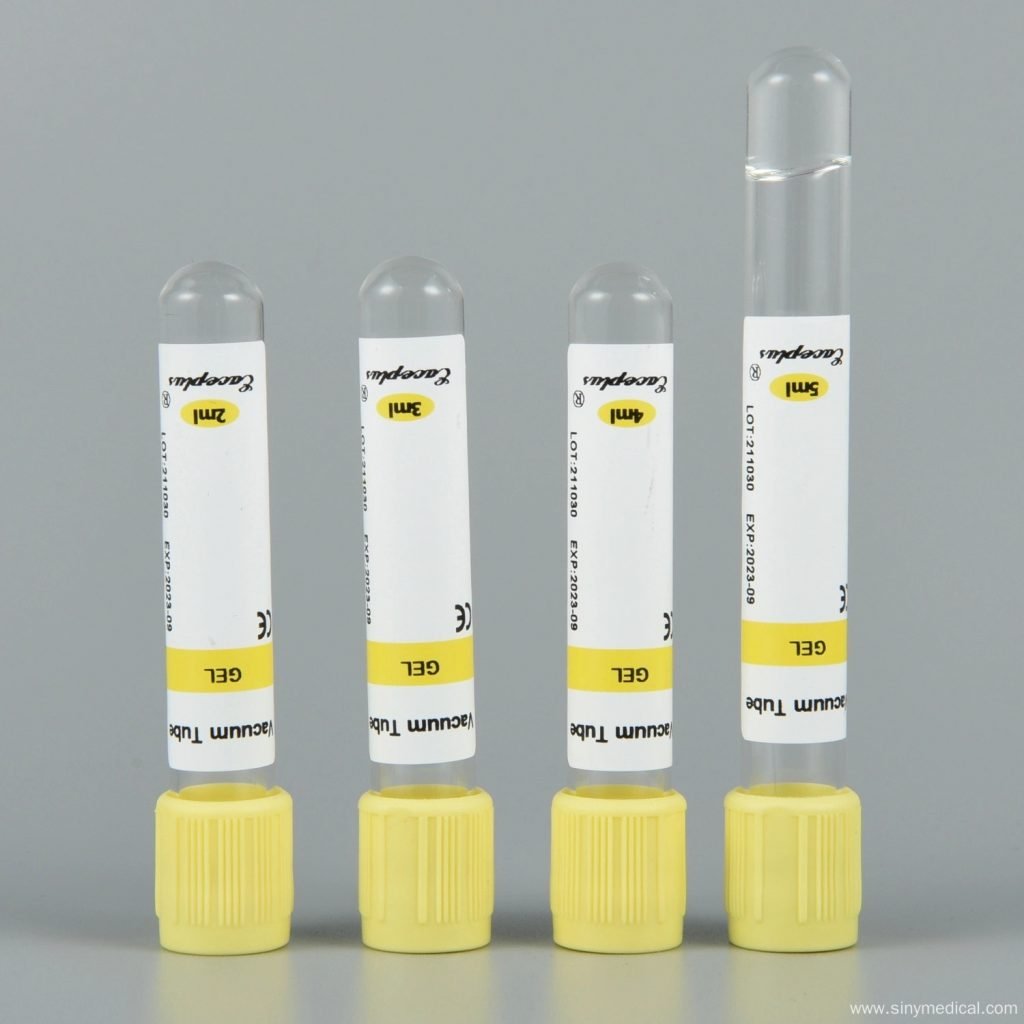
Characteristics of Yellow Cap Blood Tubes
- Additives: Yellow cap tubes may contain different additives depending on their intended use:
- Acid Citrate Dextrose (ACD): An anticoagulant used to prevent clotting by chelating calcium ions. Common in blood banking and DNA testing.
- Clot Activator and Gel Separator: Used for serum separation, where the gel forms a barrier between serum and blood cells after centrifugation.
- Sodium Citrate or Heparin: Less common but used for specific plasma-based tests.
- Material: Available in PET or glass, ensuring compatibility with various laboratory equipment.
- Vacuum System: Ensures precise blood collection for consistent results.
- Color Coding: The yellow cap indicates the presence of specific additives, making it easy to identify.
How Yellow Cap Tubes Work
The function of a yellow cap tube depends on its additive:
- ACD Tubes: These prevent clotting, preserving whole blood or plasma for tests like blood typing, crossmatching, or DNA extraction. After collection, the tube is gently inverted to mix the blood with the anticoagulant.
- Gel Separator Tubes: These contain a clot activator to speed up clotting and a gel that forms a barrier during centrifugation, separating serum from blood cells. This ensures clean serum samples for biochemical testing.
Common Tests Using Yellow Cap Tubes
Yellow cap tubes are used for a variety of specialized and routine tests, including:
- Blood Bank and Transfusion Studies: Blood typing, crossmatching, and compatibility testing for transfusions.
- HLA Typing: Human Leukocyte Antigen typing for organ transplantation and immunogenetic studies.
- Molecular Diagnostic Testing: DNA extraction for PCR assays and genetic testing.
- Platelet Aggregation Studies: Analysis of platelet function in hematology.
- Virology Studies: Detection of viral infections using plasma samples.
- Biochemical Tests: Liver function tests, lipid profiles, and electrolyte assays (when using gel separator tubes).
Advantages of Yellow Cap Tubes
- Versatility: Suitable for both plasma and serum-based tests, depending on the additive.
- Efficient Separation: Gel separator tubes provide clean serum samples, reducing the risk of contamination.
- Preservation: ACD tubes preserve blood components for extended periods, ideal for blood banking and genetic testing.
- Accuracy: Additives ensure sample stability, leading to reliable test results.
Best Practices for Using Yellow Cap Tubes
- Inversion: Gently invert ACD tubes 8–10 times immediately after collection to mix the anticoagulant with the blood. For gel separator tubes, invert 5–6 times to activate the clot activator.
- Filling: Ensure the tube is filled to the recommended level to maintain the proper blood-to-additive ratio.
- Centrifugation: Follow laboratory guidelines for centrifugation speed and time to achieve optimal separation.
- Storage: Store ACD tubes at room temperature or as specified, and process gel separator tubes promptly to avoid hemolysis.
Discover the reliability of Siny Medical Yellow Cap Blood Collection Tubes for your laboratory needs.
Differences Between Red and Yellow Cap Blood Tubes
To help you choose the right tube for your diagnostic needs, here’s a detailed comparison of red cap and yellow cap blood tubes based on additives, uses, sample type, and processing.
| Feature | Red Cap Blood Tubes | Yellow Cap Blood Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Additives | No additives (plain tubes). | ACD anticoagulant, clot activator with gel separator, or other additives (e.g., sodium citrate). |
| Sample Type | Serum (after clotting and centrifugation). | Plasma (ACD tubes) or serum (gel separator tubes). |
| Primary Uses | Biochemical tests, serological tests, immunological assays. | Blood banking, DNA testing, HLA typing, virology, biochemical tests (gel separator). |
| Clotting | Blood clots naturally (30–60 minutes). | Prevented (ACD tubes) or accelerated (gel separator tubes). |
| Centrifugation | Required to separate serum from clot. | Required for gel separator tubes; optional for ACD tubes depending on the test. |
| Sample Stability | Serum stable for several hours; less suitable for cellular components. | Plasma or whole blood stable for longer (ACD); serum stable with gel barrier. |
| Common Tests | Liver function, lipid profiles, hormone assays, hepatitis testing. | Blood typing, DNA extraction, platelet studies, biochemical assays. |
| Processing Time | Longer due to natural clotting time. | Faster for gel separator tubes; immediate for ACD tubes. |
Why Choose Siny Medical for Blood Collection Tubes?
With years of manufacturing expertise, Siny Medical offers a complete line of CE and ISO-certified vacuum blood collection tubes. Their range of products is designed for accuracy, reliability, and safety, ensuring you get top-notch results every time.
From their Yellow Cap Blood Tubes to their Red Top No Additive Tubes, every product goes through rigorous quality checks.
Plus, their products are globally accessible through Made-in-China and showcased regularly on their YouTube Channel.
Summary
Red cap and yellow cap blood tubes are indispensable tools in medical diagnostics, each serving distinct purposes based on their additives and intended tests. Red cap tubes, with no additives, are ideal for serum-based tests like liver function, lipid profiles, and serological assays. Yellow cap tubes, with additives like ACD or gel separators, cater to plasma-based tests (e.g., blood banking, DNA testing) or enhanced serum separation for biochemical assays. Understanding their differences—additives, sample type, processing, and applications—is crucial for accurate diagnostics.
At Siny Medical, we provide high-quality blood collection tubes designed to meet the diverse needs of healthcare professionals. Whether you’re performing routine tests or specialized diagnostics, our red cap tubes and yellow cap tubes ensure reliability and precision.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between red cap and yellow cap blood tubes?
Red cap tubes contain no additives and are used to collect serum after natural clotting, ideal for biochemical and serological tests. Yellow cap tubes may contain ACD anticoagulant or clot activator with gel separator, used for plasma-based tests (e.g., blood banking, DNA testing) or serum tests with enhanced separation.
2. Can yellow cap tubes be used for the same tests as red cap tubes?
Yellow cap tubes with gel separators can be used for similar serum-based tests as red cap tubes, such as liver function tests. However, yellow cap ACD tubes are specific to plasma or whole blood tests, like blood typing and DNA extraction, which red cap tubes cannot support.
3. How should yellow cap tubes be handled after collection?
For ACD tubes, gently invert 8–10 times to mix the anticoagulant. For gel separator tubes, invert 5–6 times to activate the clot activator. Ensure proper filling and centrifuge according to laboratory guidelines.
4. Why are yellow cap tubes preferred for blood banking?
Yellow cap tubes with ACD prevent clotting, preserving whole blood or plasma for blood typing, crossmatching, and transfusion compatibility testing, making them ideal for blood bank applications.
5. Where can I purchase high-quality red and yellow cap blood tubes?
Siny Medical offers a wide range of blood collection tubes, including red cap and yellow cap tubes. Contact us at Siny Medical Contact for inquiries.



























































