Micro capillary tubes are utilized in various scientific and medical applications, where they play an essential role. These tiny tubes, with lengths ranging from meters to meters, have a wide range of uses, from experiments and research to deliver precise amounts of fluids. In this complete guide, we will explore the feature, applications, and benefits of micro capillary tubes.
Table of Contents
- 1 Micro Capillary Tube Manufacturer
- 2 1. Introduction to Micro Capillary Tubes
- 3 2. The Construction of Micro Capillary Tubes
- 4 3. Types of Micro Capillary Tubes
- 5 4. Applications of Micro Capillary Tubes
- 6 5. Advantages of Micro Capillary Tubes
- 7 6. Factors to Consider When Choosing Micro Capillary Tubes
- 8 7. Handling and Maintenance of Micro Capillary Tubes
- 9 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Micro Capillary Tube Manufacturer
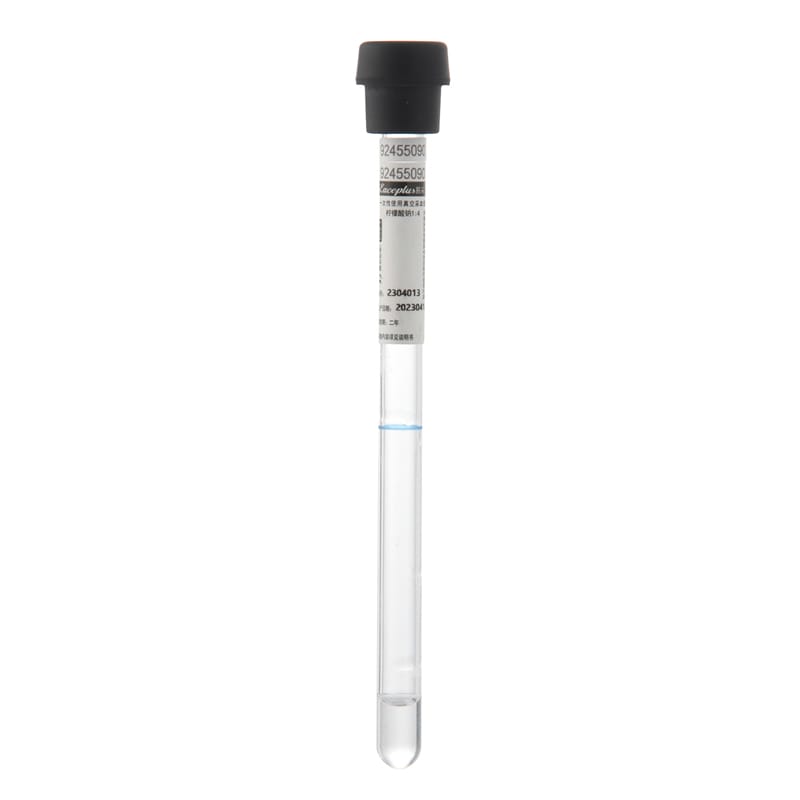
This Blood Collection Micro Capillary tube is ideal for use in a variety of laboratory settings. It intends to obtain a small amount of blood from a patient while ensuring the sample is pure and free from contamination. The tube comprises sturdy, break-resistant plastic and a unique capillary design that accurately and precisely collects samples.
- Introduction to Micro Capillary Tubes
- The Construction of Micro Capillary Tubes
- Types of Micro Capillary Tubes
- Glass Capillary Tubes
- Plastic Capillary Tubes
- Quartz Capillary Tubes
- Applications of Micro Capillary Tubes
- Scientific Research
- Medical and Diagnostic Procedures
- Industrial Processes
- Advantages of Micro Capillary Tubes
- Accurate and Precise Fluid Transfer
- Minimal Sample Contamination
- Compatibility with Various Substances
- Factors to Consider When Choosing Micro Capillary Tubes
- Diameter and Length
- Material Selection
- Surface Coatings and Treatments
- Handling and Maintenance of Micro Capillary Tubes
- Proper Cleaning Techniques
- Storage and Preservation
- Disposal of Used Tubes
- Safety Precautions when Using Micro Capillary Tubes
- Avoiding Breakage and Injury
- Protection Against Chemicals and Biohazards
- Proper Waste Disposal
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction to Micro Capillary Tubes
Materials such as glass, plastic, or quartz are used to build microvessel tubes, to enable precise transfers of liquids and gases. These tubes find deep use in scientific lap, medical procedures, and company applications where integrity and control over fluid delivery are crucial.

2. The Construction of Micro Capillary Tubes
Microcapillary tubes are usually created using focused methods that allow for exact size control. The construction process requires heating and pulling the material to create a thin tube with uniform sizes. As a result, capillary tubes have a high aspect ratio, meaning their length is significantly bigger than their lengths.
3. Types of Micro Capillary Tubes
Glass Capillary Tubes
Due to their superior chemical resistance and clarity, scientists frequently utilize glass capillary tubes. Glass capillary tubes find frequent application in scientific investigations, including chromatography, electrophoresis, and microinjection tests.. Glass capillary tubes can withstand high temperatures and are suitable for applications requiring heating or cooling.
Plastic Capillary Tubes
Plastic capillary tubes offer flexibility and affordability. They are frequently utilized in medical and diagnostic operations, including blood samples and different laboratory tests. Plastic capillary tubes are disposable, reducing the risk of cross-contamination between samples.
Quartz Capillary Tubes
Quartz capillary tubes are highly resistant to extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. They are commonly used in analytical chemistry, where high-purity materials are required. For applications requiring flame atomic absorption spectroscopy and UV-Vis spectroscopy, quartz capillary tubes are particularly beneficial.
4. Applications of Micro Capillary Tubes
Micro capillary tubes have a wide range of applications in different fields. Here are some notable examples:
Scientific Research
In scientific laboratories, siny medical tubes are used for tasks such as sample collection, fluid transfer, and precise dispensing. They play a crucial role in various experiments, including DNA sequencing, protein analysis, and cell manipulation techniques.
Medical and Diagnostic Procedures
Micro capillary tubes find extensive use in medical and diagnostic procedures. They are employed for tasks like collecting blood samples, measuring hematocrit levels, and conducting tests for various diseases and infections. Microcapillary tubes enable healthcare professionals to obtain accurate and reliable results.
Industrial Processes
Micro capillary tubes are utilized in industrial processes that require precise control over fluid dispensing and analysis. Microcapillary tubes are used in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and chemical manufacture for activities like quality monitoring, formulation development, and process optimization.

5. Advantages of Micro Capillary Tubes
Micro capillary tubes offer several advantages over other methods of fluid transfer and measurement. Some key benefits include:
Accurate and Precise Fluid Transfer
Micro illary tubes’ small size makes it possible to handle liquids and gases with accuracy and precision. Their high aspect ratio facilitates controlled delivery of minute volumes, ensuring minimal waste and accurate results.
Minimal Sample Contamination
Micro capillary tubes are designed to minimize sample contamination, making them ideal for applications requiring high purity. They provide a sealed environment that protects the sample from external contaminants and reduces the risk of cross-contamination between samples.
Compatibility with Various Substances
Micro capillary tubes are compatible with many substances, including aqueous solutions, organic solvents, and viscous liquids. They offer excellent chemical resistance and can withstand aggressive or corrosive materials, making them suitable for diverse applications.
6. Factors to Consider When Choosing Micro Capillary Tubes
A number of factors should be considered when choosing micro capillary tubes for a particular application:
Diameter and Length
The diameter and length of the capillary tube should be chosen based on the desired volume of fluid transfer. Smaller diameters provide finer control over volumes, while longer tubes allow for more extended reach.
Material Selection
The choice of material depends on the chemical compatibility requirements and the specific application. In contrast to plastic and quartz capillary tubes, which have clear advantages for certain applications, glass capillary tubes are appropriate for broad laboratory use.
Surface Coatings and Treatments
Some medical miniature blood collection vessels For children come with surface coatings or treatments to enhance functionality. For example, hydrophobic coatings can reduce liquid adhesion, improving sample recovery. Surface treatments can also modify the wettability or electrical properties of the tube.
7. Handling and Maintenance of Micro Capillary Tubes
Proper handling and maintenance are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of micro capillary tubes. Consider the following guidelines:
Proper Cleaning Techniques
Micro capillary tubes should be cleaned carefully to avoid sample carryover or cross-contamination. Rinse them thoroughly with appropriate cleaning agents, such as detergents or solvents, and ensure complete drying before reuse or storage.
Storage and Preservation
To prevent damage, one should store microcapillary tubes in a clean and dry environment. It is recommended to store them in labeled storage or racks, providing protection against physical damage or exposure to harmful materials.
Disposal of Used Tubes
Used micro vein tubes should be disposed of safely and responsibly. Follow local regulations for properly disposing of laboratory waste, including recycling options.
8. Take Care When Using to Avoid Accidents
When using microcapillary tubes, it is crucial to follow safety precautions to ensure the well-being of individuals and maintain the integrity of experiments or procedures. Here are some essential safety measures to keep in mind:
- Handle with Care: Micro capillary tubes are delicate and can break easily. Handle them gently, holding them at the ends rather than applying pressure to the fragile middle section. Avoid dropping or mishandling the tubes to prevent breakage and potential injury.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with micro capillary tubes. This typically includes gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat or protective clothing. PPE provides a barrier against potential hazards and protects against chemical splashes or biohazard exposure.
- Avoid Direct Contact with Substances: Be cautious when working with hazardous or toxic substances. Avoid direct contact between your skin and the substances being transferred through the capillary tubes. Take necessary precautions to prevent spills or leaks that could lead to exposure.
- Proper Waste Disposal: Dispose of used microcapillary tubes safely and responsibly. Follow local regulations and guidelines for the proper disposal of laboratory waste. Dispose of biohazardous waste and hazardous materials in designated containers according to established protocols.
Prevent Cross-Contamination:
- To prevent cross-contamination between samples, ensure proper cleaning and sterilization of the micro capillary tubes. Thoroughly clean the tubes after each use using appropriate cleaning agents and techniques. Pay attention to ensuring that no residues or contaminants remain inside the tubes.
- Chemical Handling: When working with chemicals, always follow appropriate handling procedures. Read and understand the safety data sheets (SDS) for the used chemicals. Take necessary precautions to prevent spills, inhalation, or skin contact. Use fume hoods or adequate ventilation when handling volatile or hazardous substances.
- Proper Training: Ensure that individuals using micro capillary tubes are adequately trained in handling, usage, and safety protocols. Adequate training and knowledge of the specific procedures and hazards associated with the work are essential to minimize risks.
- Emergency Preparedness: Familiarize yourself with the location and proper use of emergency equipment, such as eyewash stations and safety showers. In the event of an accident or exposure, know the appropriate actions and where to seek immediate medical assistance if necessary.
Avoiding Breakage and Injury
Micro capillary tubes are fragile
nd can break easily if mishandled. Take caution when handling micro capillary tubes to avoid breakage and potential injury. Hold them gently at the ends, away from the fragile middle section, and avoid applying excessive force or pressure.
Protection Against Chemicals and Biohazards
Wear the appropriate personal protection equipment (PPE) when handling toxic or hazardous material. This includes gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats. Microcapillary tubes may come into contact with potentially harmful materials, so take appropriate precautions to protect yourself and prevent contamination.
Most Blood Collection Tubes Contain An Additive That Speeds Up Blood Clotting (Clot Activator) Or Prevents Blood Clotting (Anticoagulant). The Tube That Contains The Clot Activator Produces A Serum Sample When Centrifugation separates the Blood, And The Tube That Contains The Anticoagulant Produces A Plasma Sample After Centrifugation. Some Tests Require The Use Of Serum, Some Require Plasma, And Other Tests Require Anticoagulated Whole Blood.
Proper Waste Disposal
Dispose of used micro capillary tubes according to local regulations and guidelines. If they have come into contact with biohazardous materials, follow proper disposal protocols for biohazard waste. If the tubes contain chemicals or other hazardous substances, dispose of them in designated waste containers or consult local waste management facilities for proper disposal procedures.
In conclusion,
micro fluid tubes are vital tools in scientific, medical, and industrial settings. Their small size and precise fluid handling capabilities make them indispensable for a wide range of applications. From scientific research and medical diagnostics to industrial processes, micro fluid tubes offer accurate and controlled fluid transfer, minimizing sample contamination and ensuring reliable results.
By understanding the construction, types, applications, advantages, and proper handling of micro capillary tubes, researchers, medical professionals, and industrial workers can effectively utilize these tools in their respective fields. When considering specific requirements, one should make the choice of sizes, lengths, and selected materials. Proper cleaning, storage, and disposal techniques contribute to the longevity and performance of microcapillary tubes.
First and foremost, it is important to follow safety precautions and guidelines to prevent accidents and protect personnel when working with microfluid tubes. Furthermore, mishandling can lead to breakage and potential injury. Furthermore, individuals should utilize gentle handling and appropriate personal protective equipment to ensure safety. Additionally, implementing these measures significantly reduces the risk of accidents. Moreover, adhering to these guidelines not only safeguards personnel but also preserves the integrity of the microfluid tubes. Lastly, it is crucial for everyone to understand that we must prioritize the well-being of everyone involved equally. Therefore, everyone should strictly adhere to safety protocols.
Micro arterial tubes offer a high level of detail and control, allowing for accurate fluid transfer in applications ranging from scientific experiments to medical procedures and industrial processes. Their compatibility with various items and minimal sample contamination make them invaluable tools for achieving reliable and consistent results.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the common sizes of micro capillary tubes? Micro capillary tubes come in various sizes, ranging from micrometers to millimeters in diameter.
- Can one sterilize microcapillary tubes? One can sterilize microcapillary tubes using the proper techniques, such as autoclaving or chemical sterilization.
- Are micro capillary tubes reusable?It depends on the type of capillary tube.After properly cleaning and sterilizing them, one can reuse glass and quartz capillary tubes.. However, in order to prevent cross-contamination, plastic capillary tubes are normally disposable and designed for single use.
- How do I measure the volume of liquid in a micro capillary tube? Measuring the volume in a micro capillary tube can be challenging due to the small dimensions. One common method is to use the length of the liquid column in the tube. Knowing the internal diameter and length of the tube allows for the calculation of the volume using appropriate formulas.
- Can one use micro capillary tubes with viscous substances? Yes, one can use micro capillary tubes with viscous substances.However, it is important to consider the diameter of the capillary tube, as extremely viscous liquids may have difficulty flowing through narrow tubes. Choosing an appropriate tube diameter will ensure smooth and accurate fluid transfer.